CampusConnect Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
CampusConnect is adapted from the AddressBook Level-3 created by the SE-EDU initiative.
Below are the Java libraries used in this project:
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
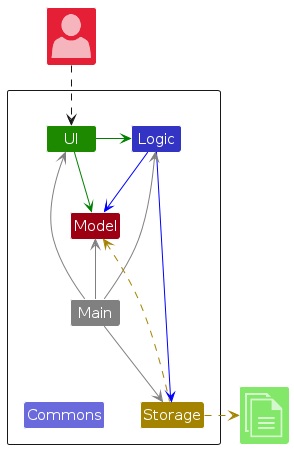
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the App.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of the App in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
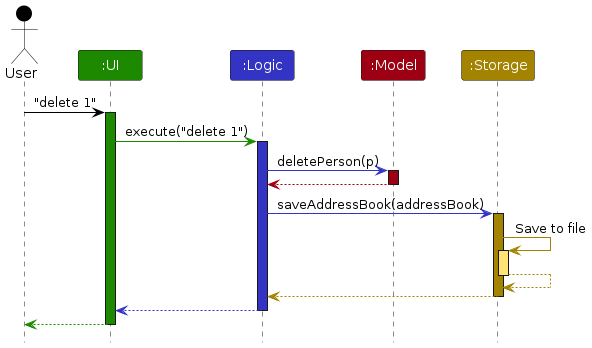
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
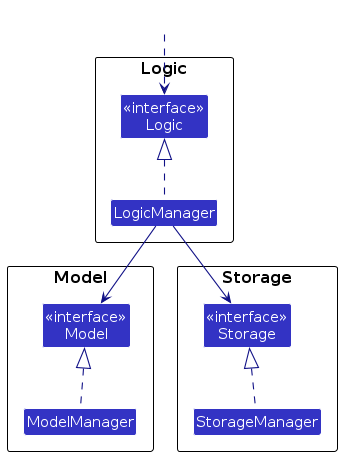
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
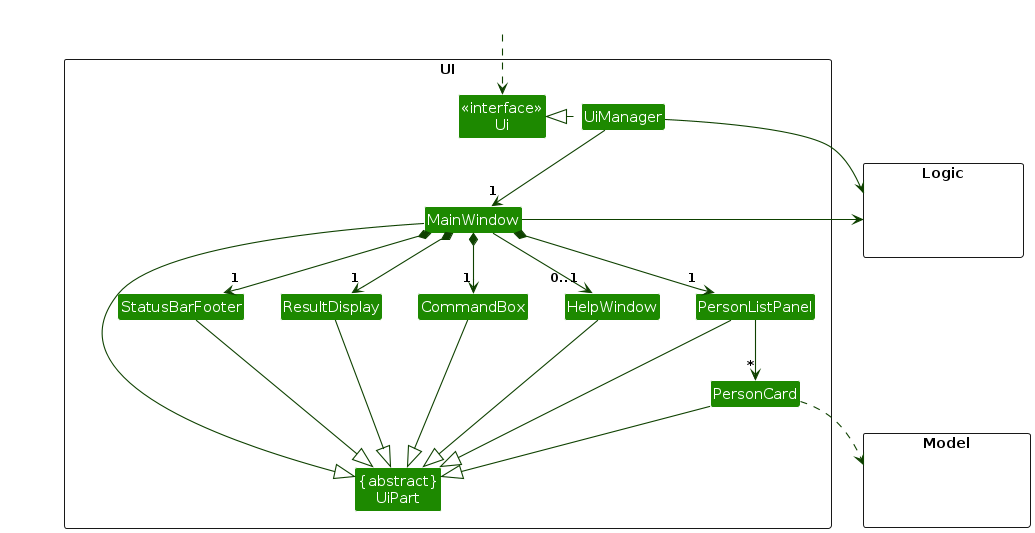
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonobject residing in theModel.
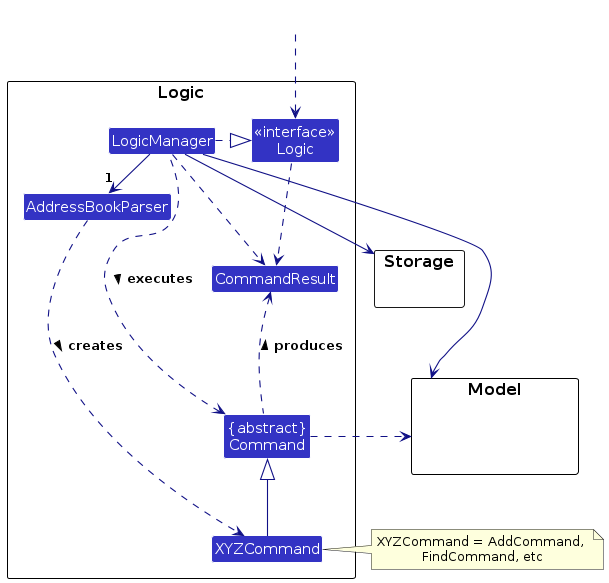
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
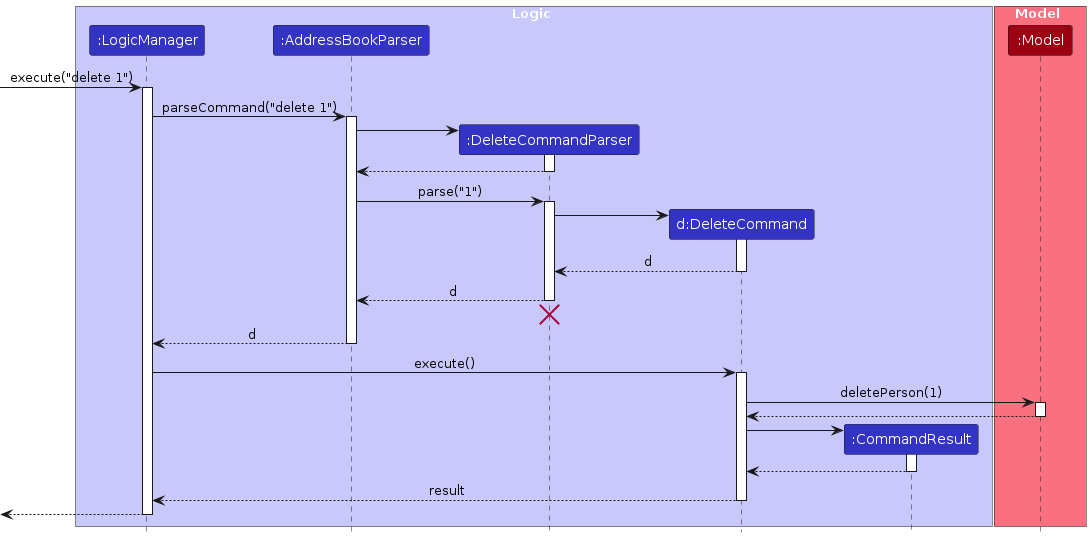
Note: The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a person). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
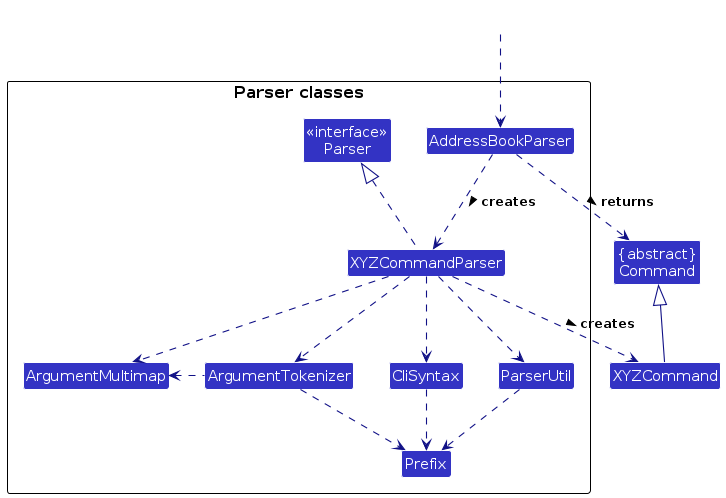
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
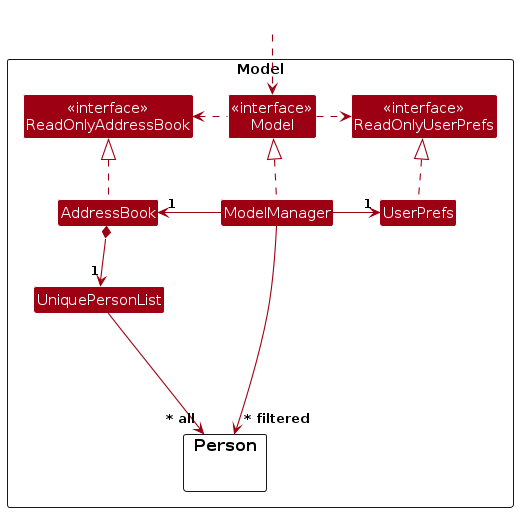
Model component
API : Model.java
Here's a class diagram of the Model component:
Below is a class diagram on the Person class and the classes related to its attributes:
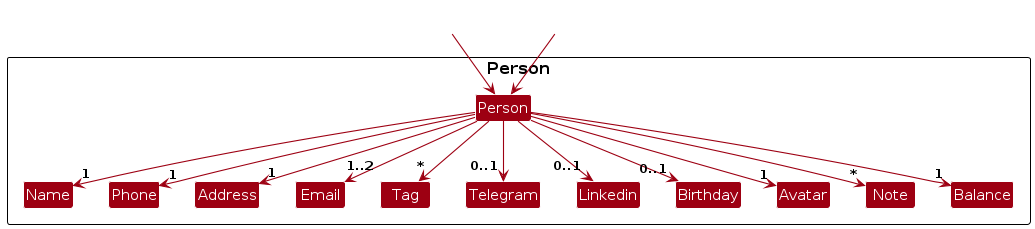
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
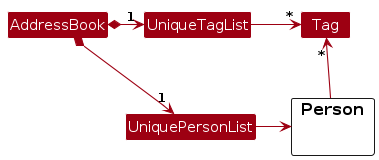
Note: An alternative (arguably, a more OOP) model is given below. It has a Tag list in the AddressBook, which Person references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag objects.
Storage component
API : Storage.java
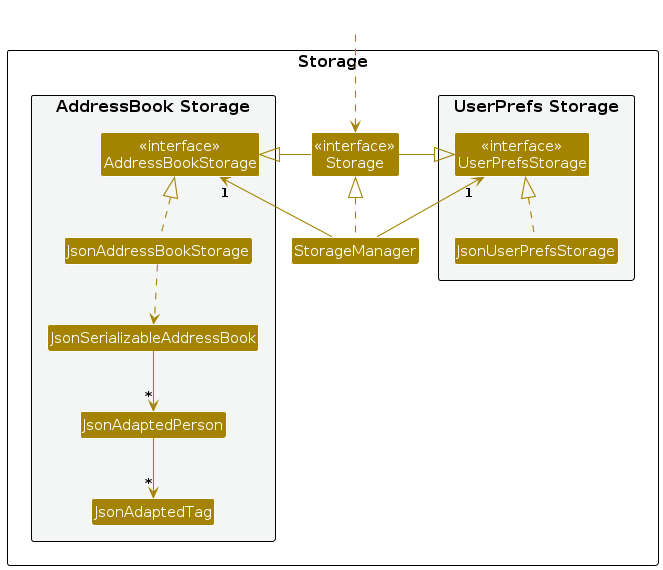
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Notifications feature
Implementation
The notifications feature is centered around Event instances.
Event can represent any type of event with a specific date and time.
This could be a birthday, an upcoming meeting or a deadline.
Event also encapsulates timings where a reminder should be created.
On startup, EventFactory#createEvents(model) is used to generate Event instances from the initial state of the model.
Any future events can be added to the data model as well during runtime.
Three public methods for Event are important for its usage
Event#addMember(Person)— Adds aPersonas associated with this event.Event#addReminder(Duration)— Sets a reminder for the event oneDurationbefore the time of the actual event. For example, ifDurationis set to a day, the reminder will be a day in advance.Event#getNotificationAtTime(LocalDateTime)— Check if any notifications should be generated based on a specific time, usually the current time should be passed as the parameter.
Below is the class diagram for the Event class and it's interactions with the other classes.
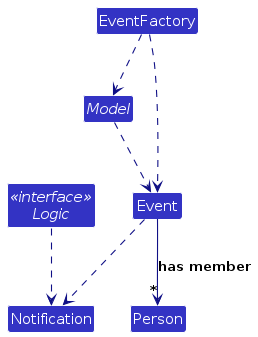
The startup sequence for creating initial events is given below as well.
On a high level, the MainApp#initEvents() will use EventFactory#createEvents(model) to generate Event instances from the intial state of the model, then add all of these events to the model.
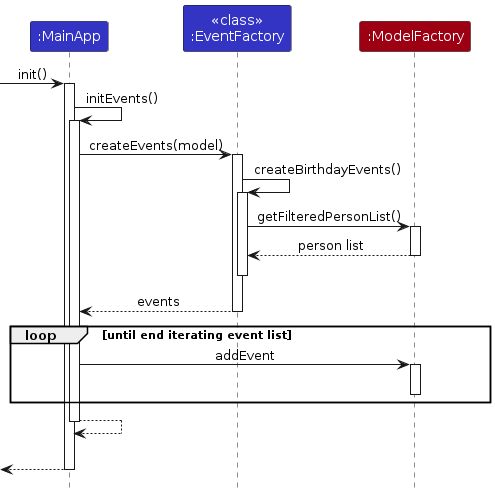
Based on the Event instances present in the data model, you can call Model#getLatestNotifications(LocalDateTime), passing in the current datetime, in order to get a list of Notification instances representing notifications that should be displayed to the user.
The UI system will make use of this API to check if any notifications should be displayed to the user at startup.
The flow for the startup notifications is described by the following sequence diagram.
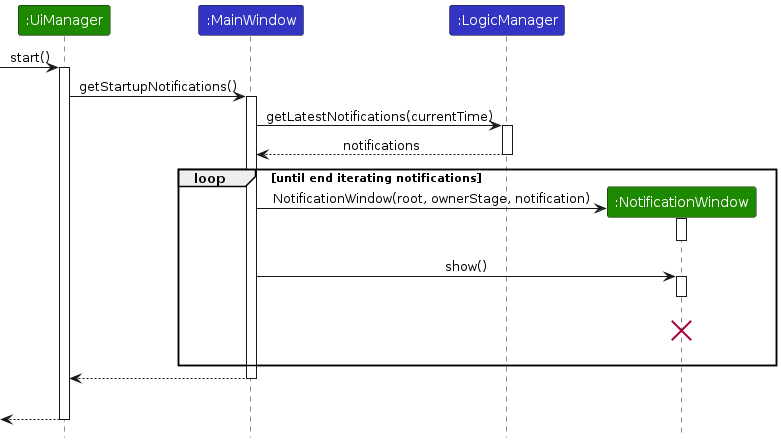
Design considerations:
Aspect: Generic design
A generic event system was created, even though CampusConnect only requires a specific Birthday notification system at the moment.
Alternative 1 (current choice): Generic event system.
- Pros: Extensible for future types of Events and Notifications beyond birthdays.
- Cons: More code required, and more indirection in code because of the generic nature.
Alternative 2: Birthday notification system.
- Pros: Simpler to implement, code will be more straightforward to understand as well.
- Cons: Any future ideas to implement new notifications and events will not benefit from the existing implementation of the birthday notification system.
AddAlt feature
Implementation Details
The addalt feature involves creating a new Person object with additional contact details to replace the previous Person object.
This is done using the AddAltPersonDescriptor class; AddAltPersonDescriptor object stores the additional contact information to be added to the previous Person object.
As a result, the existing Person class in AB3's implementation is enhanced to have the capacity of containing more attributes. The Person object is now composed of the following additional attributes due to the addalt feature on top of the existing attributes from AB3's implementation:
Email: The secondary email address of the contact.Linkedin: The linkedin of the contact.Telegram: The telegram handle of the contact.Birthday: The birthday of the contact.
The java.util.Optional<T> class is utilised to encapsulate the optional logic of the above attributes.
To add these additional attributes into a Person object, an INDEX parameter, followed by the prefixes that represent the attributes needs to be specified for the addalt command.
INDEX represents the index number of the contact to be edited in the contact list.
While all the fields are optional, at least one needs to be given to the addalt command.
The flow for the addalt command is described by the following sequence diagram:
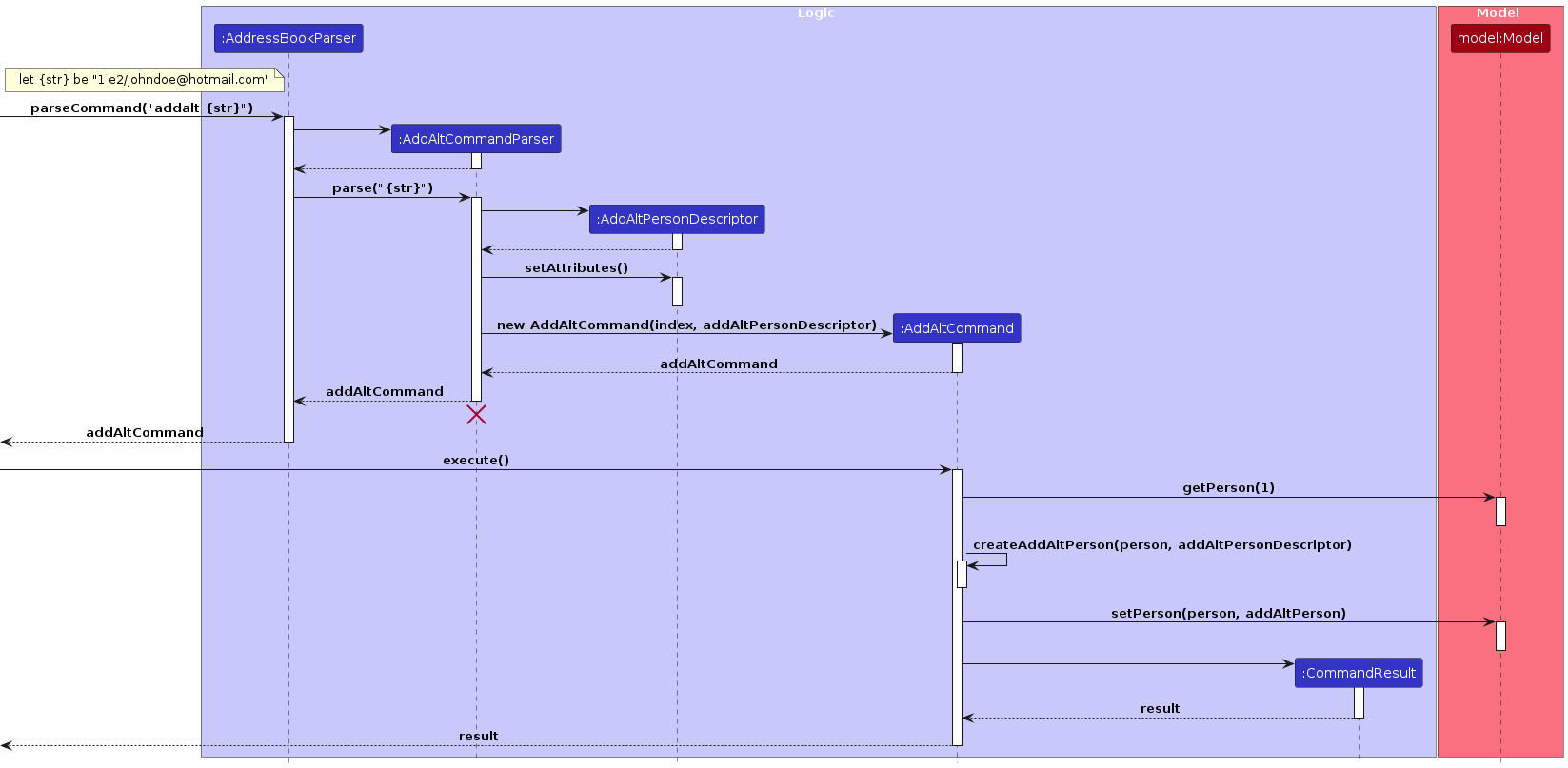
Feature details
- The application will validate the arguments supplied by the user; whether the
INDEXprovided is valid and each of the additional attribute input follows the pre-determined formats defined in their respective classes. It also checks that the added secondary email does not result in the contact to have duplicate emails. - If any of the inputs fails the validation check, an error message is provided with details of the input error and prompts the user for a corrected input.
- If all of the inputs pass the validation check, a new
Personobjected with the updated attributes is created and stored in theAddressBook.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Generic design
The additional attributes to be added into a Person object on top of the original AB3 attributes are encapsulated into their respective classes: Linkedin, Telegram and Birthday. These classes are implemented similarly to the other existing attributes of Person, but they are modified according to the respective input patterns that model the real world.
As these attributes are additional information for a Person object, every attribute has been made optional in the case when user only keys in several, but not all of the additional attributes into the command. However, the purpose of using this command only exists when users would like to add additional attributes to a Person in the contact list. Thus, the addalt command is designed to ensure that the user adds at least one of the additional attributes aforementioned.
As this command merely adds additional attributes to a Person object, this can be done by enhancing the add command.
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Create a separate command,
addalt.- Pros:
- Many cases of empty/null inputs in the optional fields need not be accounted for when saving the data and testing when a new
Personis added by theaddcommand.
- Many cases of empty/null inputs in the optional fields need not be accounted for when saving the data and testing when a new
- Cons:
- Inconveniences users as users have to key in two separate commands in order to add additional attributes of a
Person.
- Inconveniences users as users have to key in two separate commands in order to add additional attributes of a
- Pros:
- Alternative 2: Enhance the current
addcommand.- Pros:
- Improves the user's convenience by allowing them to add both compulsory and optional attributes to a new
Personentry.
- Improves the user's convenience by allowing them to add both compulsory and optional attributes to a new
- Cons:
- Many cases of empty/null inputs in the optional fields have to be accounted for when saving the data and testing.
- Pros:
Edit feature
Implementation Details
The edit feature is similar to the implementation of addalt; it involves creating a new Person object with edited contact details to replace the previous Person object.
This is done using the EditPersonDescriptor class; EditPersonDescriptor object stores the contact information to be updated to the previous Person object.
The edit command has similar input fields to the addalt command with the difference being that it is able to edit all the attributes of a Person object except:
Note: The notes of the contact. ReadNotes featurefor more details.Avatar: The profile picture of the contact. ReadUpdate photo featurefor more details.Balance: The amount that the contact owes. ReadPayments featurefor more details.
While all the fields are optional, at least one needs to be given to the edit command. Users who wishes to edit empty additional attributes of Person object should use addalt instead.
Feature details
- Similar to
addalt, the application will validate the arguments supplied by the user; whether theINDEXprovided is valid and each ofPersonattribute input follows the pre-determined formats defined in their respective classes. However, it also checks that theeditcommand does not update any empty additional attributes ofPersonand updatePersonobject to have same primary and secondary email. - If an input fails the validation check, an error message is provided which details the error and prompts the user the course of action.
- If the input passes the validation check, the application checks if the corresponding
Personand the newPersonobject with the edited attributes is the same. - If the check fails, user will be prompted that current
editcommand does not update thePersonobject. - Otherwise, a new
Personobjected with the updated attributes is created and stored in theAddressBook.
The following activity diagram shows the logic of a user using the edit command:
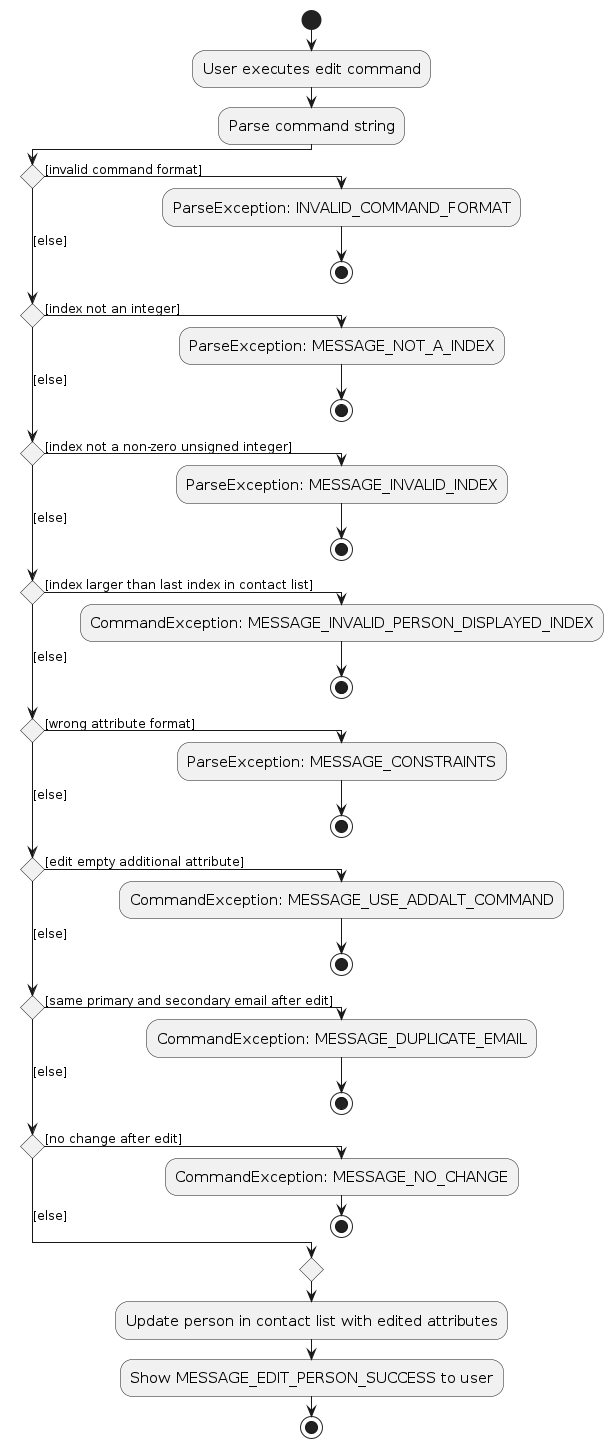
The flow for the edit command is described by the following sequence diagram:
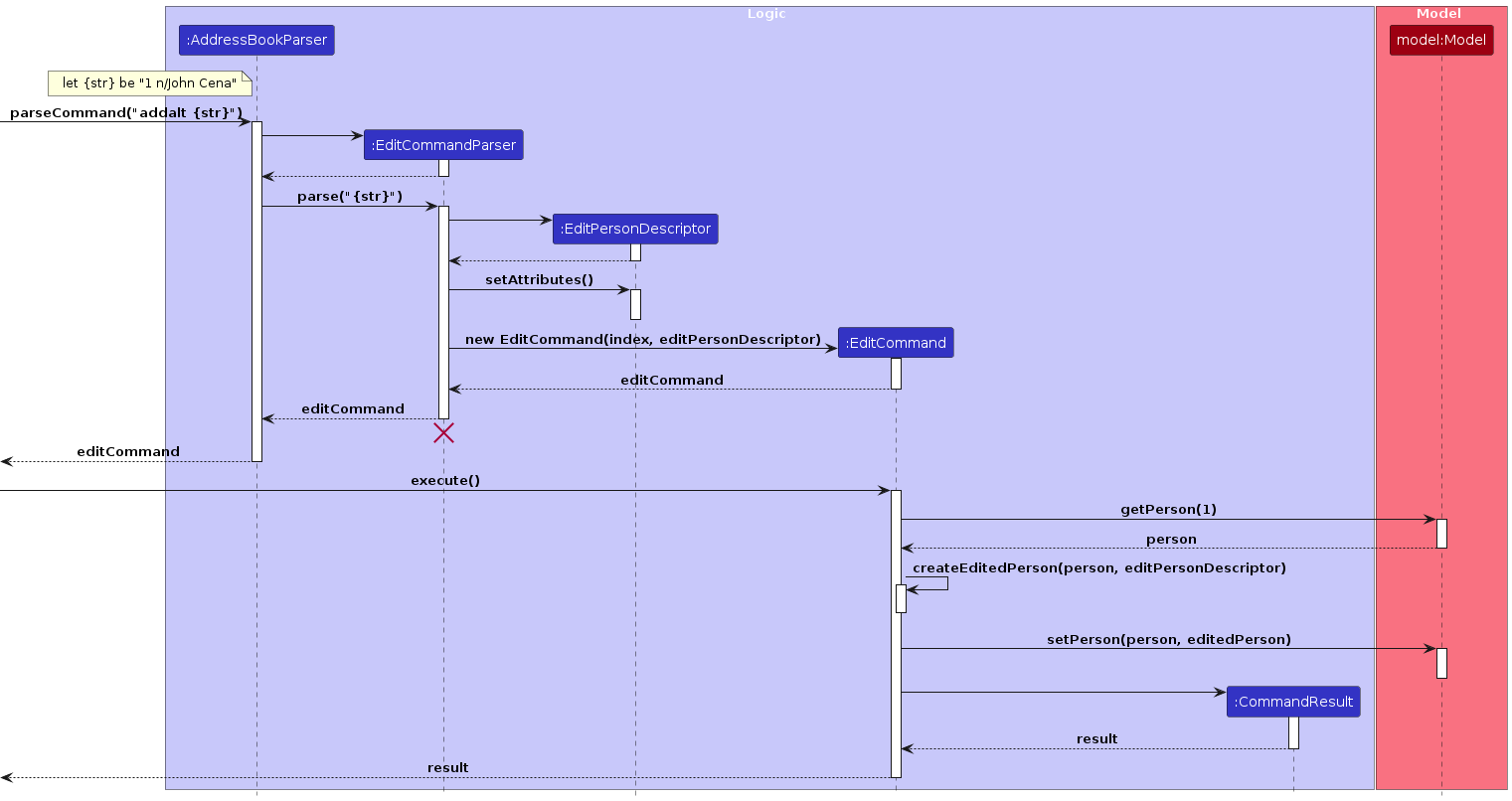
Design Considerations
Since edit command updates attributes of a Person object, setting the values directly to the Person object could be another viable option.
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Create a new
Personobject.- Pros:
- Guarantees immutability of
Personclass, reducing possible bugs.
- Guarantees immutability of
- Cons:
- Performance overhead; a
Personobject is always created even if for instance, only one attribute ofPersonobject is changed.
- Performance overhead; a
- Pros:
- Alternative 2: Set the edited attributes to the existing
Personobject.- Pros:
- Minimal performance overhead; less memory usage.
- Cons:
- More bug prone.
- Pros:
Find feature
The find command feature allows users to locate specific Person instances within the application based on keywords provided. It is significantly revamped from AB3's implementation in three ways:
- Support for all Person fields except photos, with conditions for each field set based on the most appropriate way a user would want to search for contacts using each field (instead of just word-level matching).
- Support for boolean operators, allowing users to combine multiple search criteria into an arbitrarily-complex boolean expression.
- Support for quoted strings, which allow for the use of multi-word keywords or keywords with some special characters.
This is accomplished using a custom-built tokenizer / lexer (FindFilterStringTokenizer) and parser (FindExpressionParser).
The existing FindCommandParser is used as a harness to tie the two together and provide a single entry point for the feature.
Tokenizing / Lexing
The FindFilterStringTokenizer class is responsible for parsing complex boolean find filter strings into tokens, which can later be used to construct a filter expression tree.
It is reminiscent of lexers used in interpreters and compilers, and is implemented using a state machine.
The class also includes a Token inner class that represents a token in the filter string. Each Token has a Type and a text representing the token in the filter string.
The class takes a filter string as input and tokenizes it into a list of Token objects.
Each Token object represents a component in the boolean filter string and has a Type (AND, OR, NOT, LPAREN, RPAREN, CONDITION) and a text representing the token in the filter string.
The tokenize method is the main method in this class.
It iterates over the characters in the filter string and based on the current character, it creates a new Token object and adds it to the list of tokens.
The method handles different types of tokens including AND, OR, NOT operators, parentheses for grouping, and conditions in the form of FIELD/KEYWORD or FIELD/"KEYWORDS AS QUOTED STRING".
Ultimately, the tokenize method returns a list of Token objects that represent the tokens in the filter string.
Parsing
The FindExpressionParser class is responsible for constructing a filter expression tree from a list of tokens, which is reminiscent of parsers used in interpreters and compilers.
The parseToPredicate method is the main method in this class.
It uses a recursive descent parsing algorithm to parse the list of tokens into a filter expression tree.
The class also converts it into a Predicate<Person> that can be directly used to filter the list of persons.
Specifically, the class takes a list of Token objects from FindFilterStringTokenizer and parses it into a filter expression tree.
These nodes are represented as subclasses of the ExprNode inner class, which is an abstract class that represents a node in the filter expression tree.
Each ExprNode has a Type and a text representing the node in the filter string, as well as a toPredicate method which outlines how to convert that node into a Predicate<Person> which can actually be used to filter through a person list.
The subclasses are:
BinaryOpNode: Represents a binary operation (AND,OR) between two other nodes (which can be any type of ExprNode).NotNode: Represents aNOToperation on another node (which can be any type of ExprNode).ConditionNode: Represents a condition in the form ofFIELD/KEYWORDorFIELD/"KEYWORDS AS QUOTED STRING".
The parsing conducted by the parseToPredicate method follows the structure of a boolean expression grammar, which is defined as follows:
- Expression: An expression is a term or an expression followed by
ORand a term. - Term: A term is a factor or a term followed by
ANDand a factor. - Factor: A factor is a condition, a factor preceded by
NOT, or an expression enclosed in parentheses.
This structure ensures that the AND operator has higher precedence than the OR operator, and the NOT operator has higher precedence than both AND and OR.
This is because a term (which can contain AND operations) is treated as a single unit in an expression, and a factor (which can contain NOT operations) is treated as a single unit in a term.
Ultimately, the parse method returns an ExprNode object that represents the root of the filter expression tree.
This tree structure represents the logical structure of the user's input and is used to evaluate whether a record matches the filter conditions.
The flow of the find feature is described by the following high-level sequence diagram:
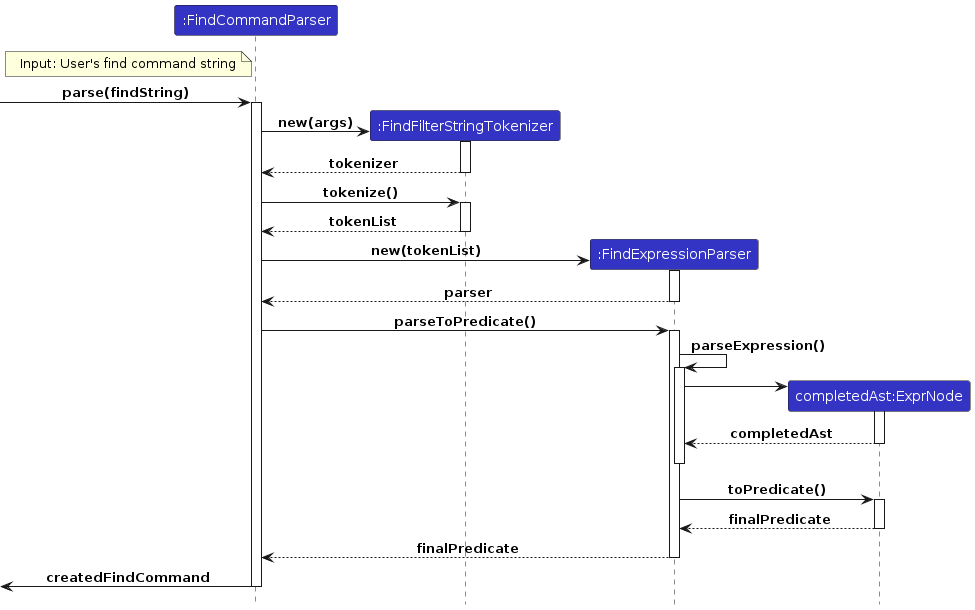
Design considerations:
Aspect: Command Flexibility vs. Complexity
Alternative 1 (current choice): Support boolean operations in
FindCommand.- Pros: Provides powerful search capabilities.
- Cons: Increases code complexity and potential for user input errors.
Alternative 2: Only allow simple keyword-based searches.
- Pros: Easier to implement and use.
- Cons: Limits user's searching abilities.
Aspect: Tokenizer library
Alternative 1 (current choice): Custom-built tokenizer and parser.
- Pros: Allows for more flexibility in terms of the syntax of the search criteria. Can handle our custom-defined terms, operators, and grouping symbols explicitly.
- Cons: More code required, requires regular maintenance to adapt to new features or changes.
Alternative 2: Use a third-party library.
- Pros: Less code required, might be more robust and have additional features.
- Cons: Less flexibility in terms of the syntax of the search criteria. May not be able to handle our custom-defined terms, operators, and grouping symbols explicitly. Might not cater explicitly to the specific requirements of the Find command. Requires integration efforts.
Aspect: Tokenization Strategy
Alternative 1 (current choice): Custom tokenizer.
- Pros: Greater control and flexibility.
- Cons: More complex to implement and maintain.
Alternative 2: Regular expression-based tokenizer.
- Pros: Can be more concise.
- Cons: May not handle all edge cases or complexities.
Aspect: Supported Logical Operators
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use standard boolean operators (
&&,||,!).- Pros: Universally recognized and understood.
- Cons: Limited to boolean logic.
Alternative 2: Support more advanced operators or functions (e.g., nearness search, regex patterns).
- Pros: Provides more power and flexibility to users.
- Cons: Significantly complicates parsing and understanding for users.
Aspect: Handling Invalid Inputs
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Throw an exception and inform the user.
- Pros: User is made aware of mistakes immediately.
- Cons: Stops the command processing.
- Alternative 2: Silently ignore or correct invalid inputs.
- Pros: Smoother user experience.
- Cons: User might not realize they made a mistake.
Update photo feature
Implementation
Command logic
The UpdatePhotoCommand feature allows users to update photo of a specific contact. This functionality is essential for forgetful users who want to store photos of contacts to remember them easier.
Two key classes are involved in this implementation:
UpdatePhotoCommand: Handles the logic for updating photo.Avatar: Represents the photo of a contact.
Photos are stored as an Avatar within the Person model.
The Avatar class contains a String representing the path to the chosen photo.
When a user inputs a command to update photo of a contact, the UpdatePhotoCommandParser parses the user input and creates a new UpdatePhotoCommand object. This object is then executed, which results in the update of the contact's photo.
The process can be summarized in the following logic flow:
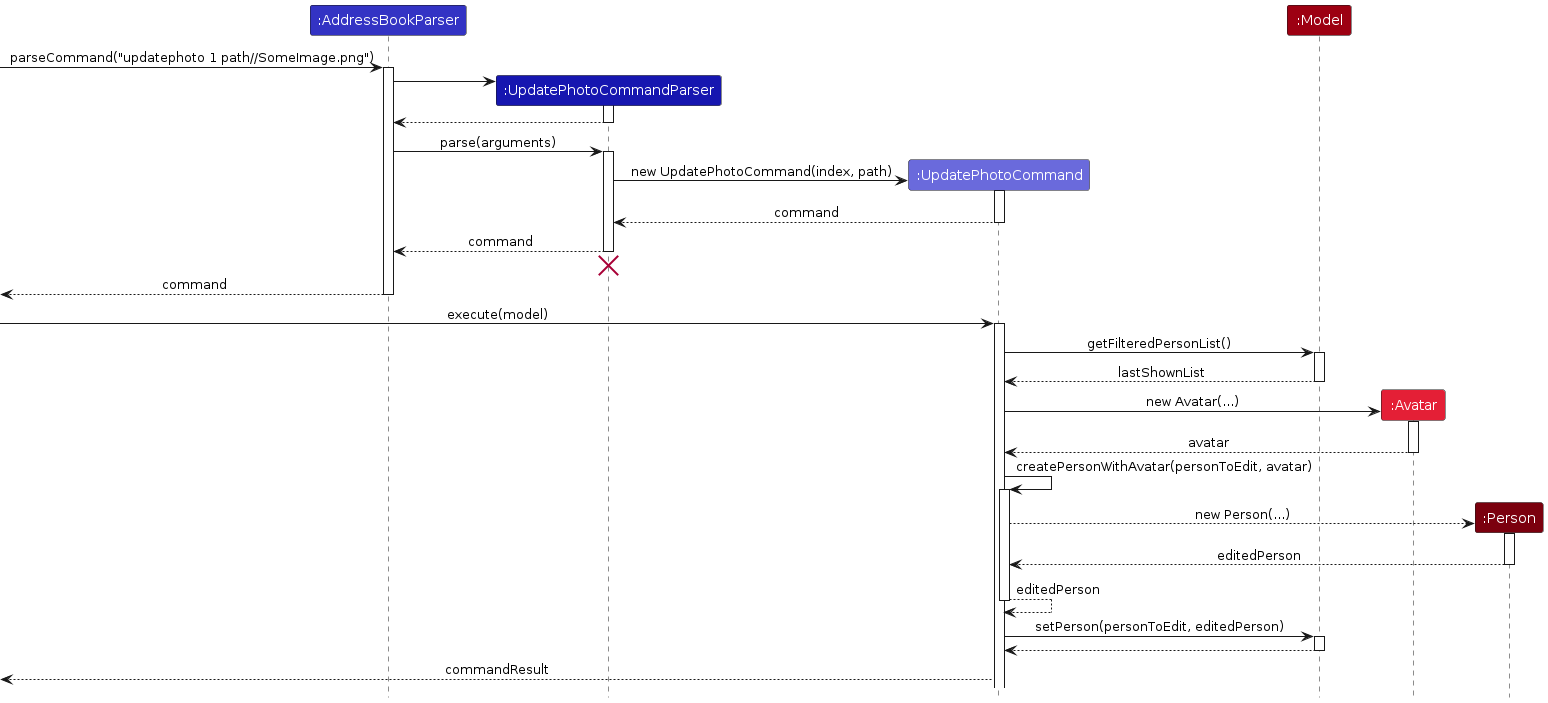
- Parse user input to create a
UpdatePhotoCommandobject. - Execute the
UpdatePhotoCommand, which involves:- Retrieving the list of all persons.
- Validating the provided index.
- Creating an exact copy of the person at the provided index, except for the
Avatar. - Replacing the specified person with their copy.
- Return a
CommandResultindicating the outcome.
Key methods in this implementation include:
UpdatePhotoCommand::UpdatePhotoCommand(Index index, String path): Constructor to initialize the command.UpdatePhotoCommand::execute(Model model): Updates the photo as well as the model.
Payments feature
Implementation
The Payments feature allows users to keep track of the money they owe to and are owed by their contacts. This feature is useful for users who want an easy way to figure out how to settle their payments in one future transaction, and ensure that all transactions are tracked and eventually settled.
Three key classes are involved in this implementation:
Balance: Represents money amounts owed by or to a contact.PayCommand: Handles the logic to track that you have paid / lent money to a contact.PaybackCommand: Handles the logic to track that you have received / borrowed money from a contact.
Additionally, the ParserUtil::parseBalance method is used to parse a human-friendly string representation of a balance into an int value representing a monetary value in cents.
Money is represented with a Balance class, which is effectively a wrapper around an int value representing a monetary value in cents. However, users interact with the Balance class through a human-friendly string representation, with a dollars and cents component, that may optionally include a dollar sign.
Most validation is handled by the Balance class, through three static methods:
isValidDollarString(String test): Checks if a given string is a valid human-friendly string representation of a balance using a validation regex.isWithinBalanceLimit(Integer balanceInCents): Checks if a given integer is a valid balance value that is a field of a contact. CampusConnect restricts users to only be able to track a maximum payment owed to / from a contact of $10,000.isWithinTransactionLimit(Integer amountInCents): Checks if a given integer is a valid money value that is used in a single transaction. Due to the $10,000 balance limit, any individual transaction cannot transact more than $20,000, since that will always lead to the balance limit being exceeded. This check occurs whenever aBalanceobject is instantiated, since there should never be anyBalanceobjects with a value greater than $20,000.
The PayCommand and OweCommand classes are extremely similar. Both classes simply update the Person's balance with the amount given.
The following activity diagram shows the logic of the validation checks that occur when a user uses the pay command:
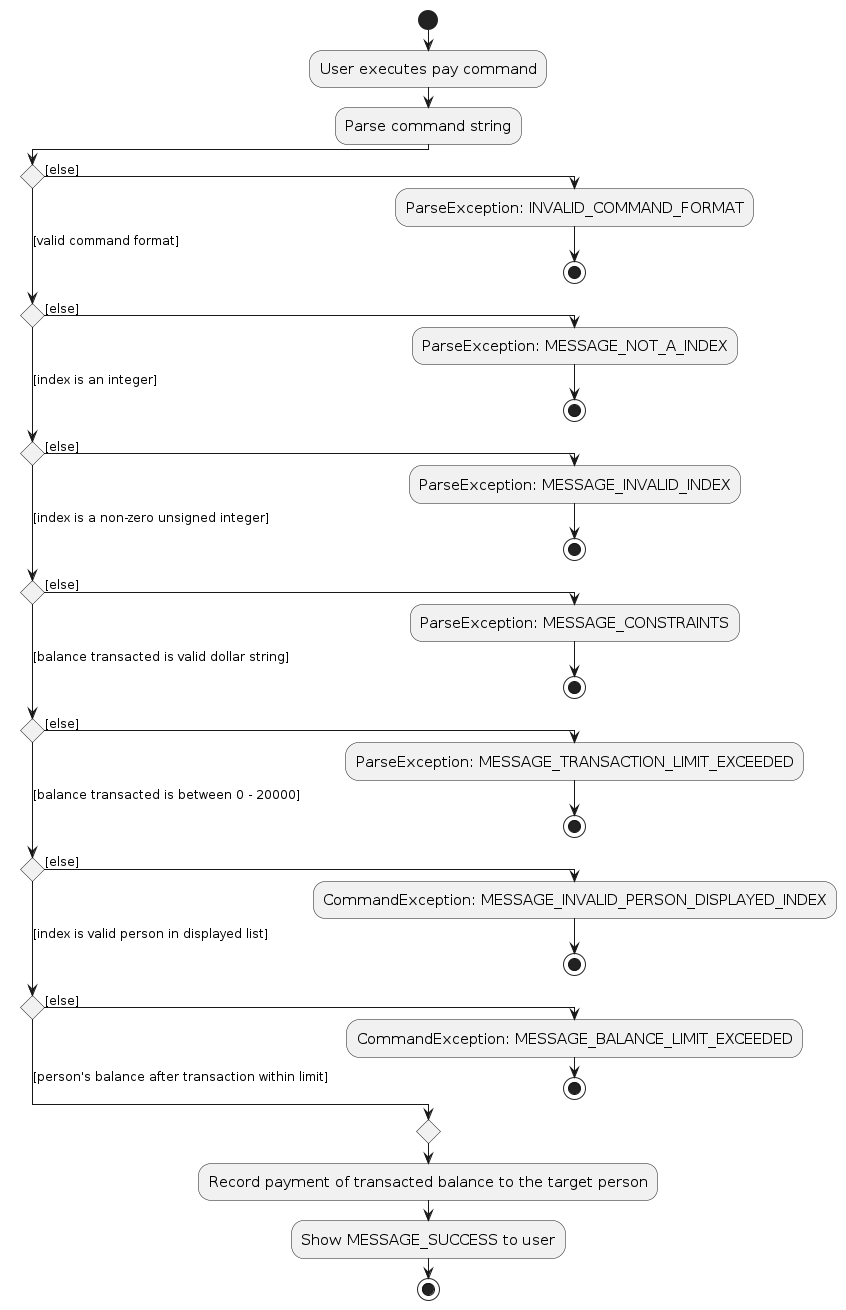
The series of validation checks in the activity diagram also applies to the owe command.
Design considerations
Aspect: Money representation data type
There are multiple options to represent money values in the application within the Balance class.
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Use
intto represent money value in cents.- Pros: Simple and straightforward, and not vulnerable to floating-point precision errors.
- Cons: Requires more complex processing when converting to human-friendly string representations.
- Alternative 2: Use
doubleto represent money value in dollars.- Pros: More human-friendly.
- Cons: Vulnerable to floating-point precision errors.
Aspect: Specialization of commands
The payments feature could be implemented as a single command, with a negative sign to specify whether the payment is a pay or owe command.
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Use two separate
payandowecommands to represent positive and negative transactions.- Pros: Make the concept more straightforward for a human to understand; humans verbalize their thoughts by saying "I pay $X to contact Y" or "I owe $X to contact Y".
- Cons: Requires users to remember two separate commands, and requires more code to implement and be maintained.
- Alternative 2: Use a single command that takes in values with negative signs.
- Pros: Only requires users to remember a single command, and less code maintenance required by maintainers.
- Cons: Less human-readable, and requires more complex processing to handle negative signs.
Notes feature
Implementation
Commmand logic
The AddNoteCommand feature allows users to add personalized notes to a specific contact in the Address Book. This functionality is essential for users who wish to record additional information about their contacts.
Three key classes are involved in this implementation:
AddNoteCommand: Handles the logic for adding the note.Index: Represents the index of the person in the filtered person list to whom the note will be added.Note: Represents the content of the note to be added.
Notes are stored as an ObservableList<Note> within the Person model. This is done to simplify storage and retrieval of notes, as well as to enable the use of JavaFX components to display the notes with the Observer pattern.
The Note class is a simple wrapper class that contains a String representing the content of the note.
When a user inputs a command to add a note, the NoteCommandParser parses the user input and creates a new AddNoteCommand object. This object is then executed, which results in the addition of the specified note to the targeted contact.
The process can be summarized in the following logic flow:
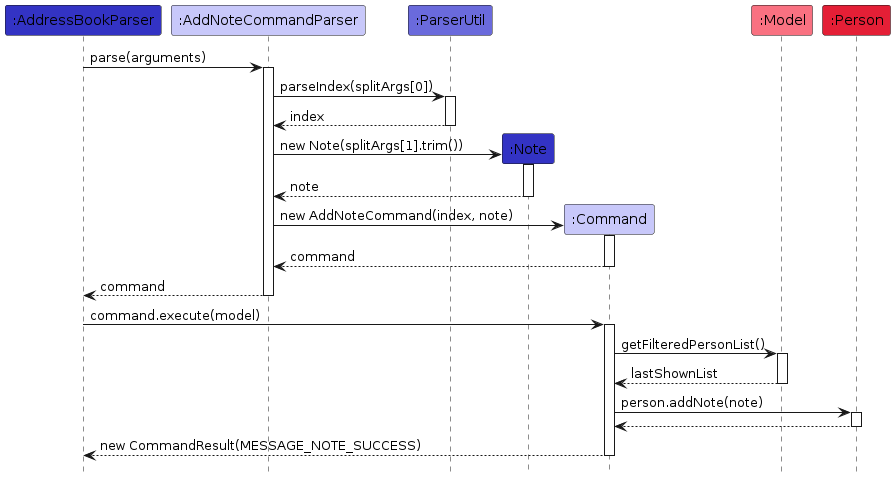
- Parse user input to create a
AddNoteCommandobject. - Execute the
AddNoteCommand, which involves:- Retrieving the list of all persons.
- Validating the provided index.
- Adding the note to the person at the specified index.
- Return a
CommandResultindicating the outcome.
Key methods in this implementation include:
AddNoteCommand(Index index, Note note): Constructor to initialize the command.execute(Model model): Adds the note and updates the model.
UI Logic
The Notes feature also includes a user interface component to allow users to interactively add, view, and remove notes from contacts.
The user interface for the Notes feature is implemented using JavaFX components. The main components include:
PersonCard: Displays individual person's details and includes a button for accessing notes.NotesWindow: A pop-up window that displays all notes associated with a person.
The PersonCard component includes a button (notesButton) that, when clicked, triggers the handleNotesButtonClick method in the controller. This method creates and shows a new NotesWindow.
The NotesWindow is responsible for displaying the list of notes and is populated using a ListView component. The controller for NotesWindow handles the population of this list and the closing of the window. NotesWindow has a button (closeButton) that, when clicked, triggers the handleCloseButtonClick method in the controller. This method closes the window. The NotesWindow is also closed when the user presses the ESC key.
Design considerations
Aspect: Integration with Existing Data Model
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Leverage existing
Personclass andModelinterface.- Pros: Utilizes existing data structures and methods, ensuring consistency and potentially reducing the likelihood of bugs.
- Cons: The
Personclass becomes more complex as more features are added.
- Alternative 2: Create a separate system for managing notes.
- Pros: Keeps the
Personclass simpler and more focused on contact information. - Cons: May result in duplication of effort and increased complexity in ensuring consistency between the contact and note systems.
- Pros: Keeps the
Choosing alternative 1 aligns with the principle of maximizing code reuse and maintaining consistency across the application, even though it slightly increases the complexity of the Person class.
Aspect: User Interaction and Experience
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Pop-up window for notes.
- Pros: Provides a clear and focused view for user to manage notes.
- Cons: Additional window management required; may be less convenient for quick interactions.
- Alternative 2: Inline editing within the
PersonCard.- Pros: Potentially more convenient for quick additions or edits.
- Cons: Could clutter the interface and distract from the main contact information.
Choosing alternative 1 provides a balance between functionality and user interface simplicity, ensuring that the notes feature does not overwhelm the main contact viewing experience.
Testing
The UI components are tested using TestFX to ensure that they behave as expected. Test cases include verifying the display of notes, interaction responses, and the proper functioning of the close button. Ensuring thorough testing is vital for maintaining the reliability and user-friendliness of the application.
Take note that UI tests have to be run on the JavaFX thread, so UI tests have to extend ApplicationTest from TestFX to run properly.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Planned Enhancements / Known Issues
- When using multiple screens, if you move the application to a secondary screen, and later switch to using only the primary screen, the GUI will open off-screen. The remedy is to delete the
preferences.jsonfile created by the application before running the application again. - When executing
add/editcommand, if you try to add/edit a new/existing contact with the same properties of another saved contact (Note: 2 names are considered the same if both of them have the same casing and whitespaces) in your contact list, CampusConnect allows you to do so. We plan to enhance theadd/editcommand such that it takes into account what makes a contact unique in your contact list. - When executing
addaltcommand, if you input other prefixes that are not accepted by the command format, the error message shown does not prompt you to remove those prefixes and adhere strictly to the command format. We will be working on this in the future to improve the specificity of error messages. - When executing commands with
PERSON_INDEX, if you did not input an appropriate index, the error message shown is generic; CampusConnect informs you the format of the command you should adhere to instead of prompting you to input a positive index. We will be working on this in the future to improve the specificity of error messages. - When executing
updatephotocommand, if thePERSON_INDEXcontains characters besides0-9, CampusConnect will be unresponsive as we assume that you will input a valid integer forPERSON_INDEX. Moreover, successful execution of the sameupdatephotocommand with the same image will still result inPhoto updatedeven though the photo is not updated. In addition, you can input multiple valid paths and the command will update your contact profile with the last image. We will be working on handling more errors and improving the specificity of messages in the future. - When executing all commands, CampusConnect only accepts printable ASCII characters. Additionally, certain commands may only accept alphanumeric input (such as name field in
addnot accepting slashes). We plan to improve our internationalization support in the future, allowing for Unicode characters to be used throughout the app since users could have contacts with names including diacritics or non-alphabetic characters (e.g. Tamil, Arabic or Chinese names). - When executing the
findcommand, if you input aFIND_EXPRESSIONthat is not accepted by the command format, the error message shows fairly general error messages. We will be working on this in the future to improve the specificity of error messages. - When executing the
findcommand, it is impossible to search for keywords that include the double-quote character (") under any circumstance. We will be working on this in the future to support searching for the double-quote character, which could appear in fields such as notes. - When executing the
findcommand, the behavior of thebalfield is not intuitive, especially for users who do not read the User Guide in-depth. We will be working on this in the future to improve the ergonomics ofbalfield, by implementing>and<operators so users can search for balance amounts below or above the keywords. - When starting the app, if data that is previously stored in
addressbook.jsonis unable to be parsed by the application as a validAddressBook(e.g. data is corrupt), the app may overwrite it on the next exit, causing data loss. We will rewrite our data storage code to be more robust when dealing with this issue by backing up data files even when they are corrupt, allowing users to retrieve them in the future.
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- is an NUS student staying on campus
- has a need to manage a significant number of contacts
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: manage contacts faster than a typical mouse/GUI driven app
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | user | add new contacts with basic contact information | keep track of the people I know. |
* * * | user | add alternative contact information such as telegram, email and linkedin | connect with friends through my preferred channels |
* * * | user | delete contacts | reduce clutter and keep my contact list organised. |
* * * | user | add notes associated with my contacts | remember important information regarding my contacts. |
* * * | user | delete notes associated with my contacts | remove unwanted information. |
* * | forgetful user | update photos for my contacts | visually remember them. |
* * * | forgetful user | add the birthday of my contact | keep track and remember my contacts’ birthdays. |
* * * | forgetful user | receive a notification when it is the day before my contact’s birthday | remember to celebrate his/her birthday. |
* * * | user | opt out of receiving notifications | keep myself from being distracted by the notifications. |
* * * | user | record money owed to a contact | remember to settle the debt. |
* * * | user | record money owed by a contact | remember to collect the money. |
* * * | user | search through my contacts based on their respective contact information | quickly access the information required. |
* * * | user | search my contacts by name | quickly find a person without scrolling through my entire list. |
* * * | user | search my contacts by phone number | identify who is calling me from an unfamiliar number. |
* * * | international in-campus resident | add Singapore’s emergency contact details | access them quickly in urgent situations. |
* * * | in-campus resident | add campus specific information to my contacts, in particular, a tag called RA (Residential Assistant) and SOS (Security Officer) | quickly reach out to them when required. |
* * * | on-campus student | quickly list the emergency contacts I have previously registered | contact them in an emergency. |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is CampusConnect and the Actor is a NUS student who stays in campus, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC1 - Add new contact
MSS
- User enters information of the new contact to be added.
- System adds the new contact into its system.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. System detects an error in the entered data.
- 1a1. System shows an error message.
- 1a2. User enters a new add request.
Steps 1a1- 1a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: UC2 - List all contacts
MSS
- User requests list all contacts.
- System shows a list of all contacts.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. System shows an empty contact list.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC3 - Add alternative information to existing contact
MSS
- User lists all contacts (UC2).
- User enters an index with alternative information to be added for an existing contact in the system.
- System adds the alternative information to the specified contact inside its system.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. System shows an empty contact list.
Use case ends. - 2a. System detects an error in the entered data.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. User enters a new addalt request.
Steps 2a1- 2a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
- 3a. System detects that the field of the specified contact is non-empty.
- 3a1. System shows an error message and prompts users to use edit command.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System shows an error message and prompts users to use edit command.
Use case: UC4 - Edit information of existing contact
MSS
- User lists all contacts (UC2).
- User enters an index and information to be edited for an existing contact in the system.
- System edits the information of the specified contact inside its system.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. System shows an empty contact list.
Use case ends. - 2a. System detects an error in the entered data.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. User enters a new edit request.
Steps 2a1- 2a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
- 3a. System detects that the additional fields of the specified contact is empty.
- 3a1. System shows an error message and prompts users to use addalt command.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System shows an error message and prompts users to use addalt command.
Use case: UC5 - Delete contact
MSS
- User lists all contacts (UC2).
- User enters an index to delete a contact from the system.
- System deletes contact inside its system.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. System shows an empty contact list.
Use case ends. - 2a. System detects an invalid index entered.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. User enters a new delete request.
Steps 2a1- 2a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
Use Case UC6 - Add note
MSS
- User lists all contacts (UC2).
- User enters an index of the specified contact alongside the note to be added.
- System adds the note to the contact.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. System detects an invalid index entered.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. User enters a new add note request.
Steps 2a1- 2a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
Use Case UC7 - Remove note
MSS
- User lists all contacts (UC2).
- User enters an index of the specified contact alongside the index of the note to be removed.
- System removes the note from the contact.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. System detects an invalid contact or note index entered.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. User enters a new remove note request.
Steps 2a1- 2a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
Use Case UC8 - Record payment
MSS
- User lists all contacts (UC2).
- User enters an index of the specified contact alongside the amount of money paid/owed to that contact.
- System records money paid/owed to the contact.
- System displays the contact with an indication of the money owed.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. System detects an invalid index entered.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. User enters a new payment request.
Steps 2a1- 2a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
- 2b. System detects an invalid payment amount entered.
- 2b1. System shows an error message.
- 2b2. User enters a new payment request.
Steps 2b1- 2b2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
Use Case UC9 - Search for contact
MSS
- User enters a search criteria to find a contact.
- System displays all contacts that match the criteria.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. System detects an invalid search criteria.
- 1a1. System shows an error message.
- 1a2. User enters a new search request.
Steps 1a1 - 1a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use Case UC10 - Update contact photo
MSS
- User lists all contacts (UC2).
- User enters an index of the specified contact alongside the file path of the new contact photo.
- System updates the contact's photo to the specified image.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. System detects an invalid index entered.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. User enters a new update photo request.
Steps 2a1- 2a2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
- 2b. System detects an invalid file path entered.
- 2b1. System shows an error message.
- 2b2. User enters a new update photo request.
Steps 2b1- 2b2 are repeated until the data entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 3.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java 11 or above installed.
- Able to hold up to 1000 contacts without a compromise in performance.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Should respond within 1 second for any command the user inputs
- Should be easy to use and navigate for the users.
- Should be able to accommodate growth and expansion. It should be easy to add new features and functionalities as needed.
- Should be easy to maintain and update through a clear and well-documented architecture, and it should be easy to troubleshoot and fix problems should they arise.
- Data stored should be persistent until removal by the user, and all contact details should be secure.
- The code should be well-organised and well-documented to ensure ease of maintenance and debugging.
- Should provide clear and easily accessible help and documentation, including FAQs and tutorials, to assist the user in using the platform effectively.
- Should be designed to prevent errors and provide clear, actionable error messages if errors occur, so that users can correct any issues.
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- Private contact detail: A contact detail that is not meant to be shared with others
Prefix summary
| Prefix | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| n/ | Name of contact | n/John Doe |
| p/ | Phone number of contact | p/98765432 |
| e/ | Email of contact | e/johndoe@gmail.com |
| a/ | Address of contact | a/16 Bukit Timah Road, S156213 |
| t/ | Tags of contact | t/friend |
| li/ | Linkedin of contact | li/john-doe |
| tg/ | Telegram handle of contact | tg/@johndoe |
| e2/ | Secondary email of contact | e2/johndoe@hotmail.com |
| b/ | Birthday of contact | b/23/10 |
| path/ | Path to the photo of contact | path/D:/images/john-doe.png |
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
Launch and shutdown
Initial launch
Download the
CampusConnect.jarfile and copy into an empty folderDouble-click the
CampusConnect.jarfile Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimal.
Saving window preferences
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
Adding a person
Adding a
Person:Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johndoe@gmail.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01
Expected: A newPersonis successfully created with name "John Doe", phone "98765432", email "johndoe@gmail.com" and address "John street, block 123, #01-01". Success details shown in the status message. Moreover, this newPersonis visible in CampusConnect.Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johndoe@gmail.com a/
Expected: No newPersonis created. Error details shown in the status message.Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johndoe@gmail.com
Expected: No newPersonis created. Error details shown in the status message.
To see if the
Personis added, use thelistcommand and verify the lastPersonin CampusConnect.
Adding alternative contact to a person
Adding alternative contact to a
Person:Prerequisites: List all
Personsin CampusConnect using thelistcommand.Test case:
addalt 1 tg/@johndoe_123 e2/johndoe@hotmail.com li/john-doe-b9a38128a b/31/10
Expected: The firstPersonin the list is added with the following alternative contact information: telegram "@johndoe_123", secondary email "johndoe@hotmail.com", linkedin "john-doe-b9a38128a" and birthday "31/10". Success details shown in the status message. The aforementioned happens only if the fields are initially empty. Otherwise, error details will be shown in status message.Test case:
addalt 1 tg/@johndoe_123 e2/
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will not be added with the following alternative contact information: telegram "@johndoe_123". Error details shown in the status message.Test case:
addalt 1 tg/@johndoe_123 tg/@johnjohn
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will not be added with the following alternative contact information: telegram "@johndoe_123" or "@johnjohn". Error details shown in the status message.
To see if the
Personis added with alternative contact information, use the find command to search for thePersonand verify the details.To know exactly what are the alternative details of a
Personthat can be added, see this.
Editing a person
Editing a
Person:Prerequisites: List all
Personsin CampusConnect using thelistcommand.Test case:
edit 1 p/98765411 e/johndoe@gmail.com
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will have phone edited to "98765411" and email edited to "johndoe@gmail.com". Success details shown in the status message.Test case:
edit 1 tg/@johndoe e2/johndoe@gmail.com
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will have telegram edited to "@johndoe" and secondary email edited to "johndoe@gmail.com" only if the fields were not initially empty; success details shown in the status message. Otherwise, error details will be shown in status message.Test case:
edit 1 tg/@johndoe_123 tg/@johnjohn
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will not have telegram edited. Error details shown in status message.
To see if the
Person's details are edited, use the find command to search for thePersonand verify the details.To know exactly what are the details of a
Personthat can be edited, see this.
Deleting a person
Deleting a person while all persons are being shown
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
listcommand. Multiple persons in the list.Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated.Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No person is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Updating photo of a person
Updating photo of a
Person:Prerequisites: List all
Personsin CampusConnect using thelistcommand.Test case:
updatephoto 1 path/docs/images/johndoe.png
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will have profile photo updated to the picture "johndoe.png". Success details shown in the status message.Test case:
updatephoto 1 path/C:/documents/test.docx
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will not have profile photo updated. Error details shown in the status message.
To see if the
Person's profile photo is updated, use the find command to search for thePersonand verify the profile photo.
Adding note to a person
Adding note to a
Person:Prerequisites: List all
Personsin CampusConnect using thelistcommand.Test case:
addnote 1 This is a sample note for the person.
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will have a new note stating "This is a sample note for the person.". Success details shown in the status message.Test case:
addnote 1 This person is very funny! 😀
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will not have a new note stating "This person is very funny! 😀". Error details shown in the status message.
To see if the new note is added to
Person, use the viewnotes command and verify the details of the notes.
Paying money to a person
Paying money to a
Person:Prerequisites: List all
Personsin CampusConnect using thelistcommand.Test case:
pay 1 10
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will be paid $10. Success details shown in the status message.Test case:
pay 1 10.555
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will not be paid $10.555. Error details shown in the status message.Test case:
pay 1 50000
Expected: The firstPersonin the list will not be paid $50000. Error details shown in the status message.
To see if the money is paid to
Person, use the find command to search for thePersonand verify the money paid.
Owing money to a person
Owing money to a
Person:Prerequisites: List all
Personsin CampusConnect using thelistcommand.Test case:
owe 1 10
Expected: You owe the firstPersonin the list $10. Success details shown in the status message.Test case:
owe 1 10.555
Expected: You will not owe the firstPersonin the list $10.555. Error details shown in the status message.Test case:
owe 1 50000
Expected: You will not owe the firstPersonin the list $50000. Error details shown in the status message.
To see if the money the
Personowes is recorded, use the find command to search for thePersonand verify the money owed.
Finding a person
Finding a
Personwhile all persons are being shown:Test case:
find n/do
Expected: CampusConnect displays a list ofPersonthat has name that contains the substringdo.Test case:
find t/friends
Expected: CampusConnect displays a list ofPersonthat has tag that is equal to the tagfriends.Test case:
find a/John street, block 123, #01-01
Expected: CampusConnect will not display anyPerson. Error details shown in the status message.Test case:
find a/"John street, block 123, #01-01"
Expected: CampusConnect will display a list ofPersonwith addressJohn street, block 123, #01-01.
Appendix: Effort
Difficulty Level
CampusConnect is an advanced extension of the foundational AB3, enriched with sophisticated new features and a more advanced UI. These enhancements are complex and significantly expand the application's functionality beyond the original AB3.
Challenges faced
Our project encountered numerous challenges:
Extending Base AB3 Functionality
- Understanding AB3's Structure: Implementing features like addalt necessitated a deep dive into the AB3 codebase to modify classes such as
Person.java. AB3's extensive codebase posed a significant learning curve. - Mastering JavaFX: Enhancements like adding tags to denote fields required us to learn JavaFX and CSS, technologies that were new to us.
Adding New Functionality to AB3
- Notification System: We developed a comprehensive notification system for event reminders, integrating it with the existing AB3 architecture.
- Profile Photo Feature: Introducing profile photos meant having to figure out what was the best way to deal with user data that was not text-based and unable to be stored within the already existing
addressbook.json. - Notes Feature: Implementing the notes feature involved creating new UI interface elements such as
NotesWindow.java, as well as figuring out how to modify already-existing UI elements likePersonCard.java. - Payments Feature: The development of the payments system required us to modify large portions of pre-existing code. Additionally, the various risk-control checks to ensure the system was robust and secure were challenging to implement.
- Search Functionality Expansion: The
findfunction was enhanced to support complex, fully expressive queries. This involved developing a custom tokenizer, parser and expression evaluator, which was a significant undertaking. - Testing Coverage Expansion with TestFX: Expanding testing coverage to include UI testing required the use of TestFX, which was a new framework that we had to pick up and learn.
Achievements
- UI Enhancements: The UI of CampusConnect has been improved beyond the AB3 baseline, improving user experience. For instance, fields are now demarcated with a tag, and the application now supports profile photos.
- New Systems: The application now features a range of new systems, including a generalized notification system and a payment tracking system. This added a lot of functionality which the base AB3 lacked, and which was useful for users of CampusConnect.
- Functionality Expansion: Numerous features of the base AB3 have been extended, resulting in a richer contact book application which is able to store more information about contacts such as their Telegram, secondary email and LinkedIn profiles.
- Search Capabilities Enhancement: The search functionality has been augmented to accommodate complex, fully expressive searches. This greatly improves the user experience as it allows users to quickly find the contacts they are looking for.
- Test Coverage: We maintained rigorous test coverage throughout our development process, only allowing PRs to be merged if they demonstrated sufficient test coverage. Additionally, we expanded our testing methodology to include UI testing, which was not present in the base AB3.
Efficiency through Reuse
- Extending AB3 Classes: We extended the
Personclass to incorporate additional data fields crucial for theaddaltfeature. - DateTime Libraries: We utilized existing DateTime libraries for efficient and correct parsing of time-related data, which improved our development speed as it meant we did not have to write our own date-time parsing code.
Overall, significant effort was spent in firstly evaluating our user requirements, and then coming up with ways in which we could extend AB3 to better suit their needs. The implementation of these features often required us to extend AB3 well beyond its original capabilities, and in some cases write entirely new systems in order to support them. Development work was carried out without sacrificing code quality, and we maintained a high standard of testing throughout the process, only merging PRs if they demonstrated sufficient test coverage.